Unique Tips About How To Detect Achondroplasia

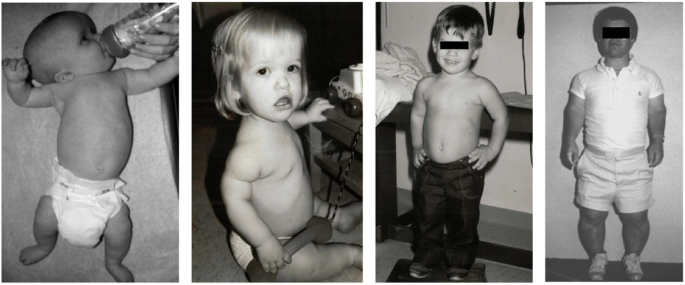
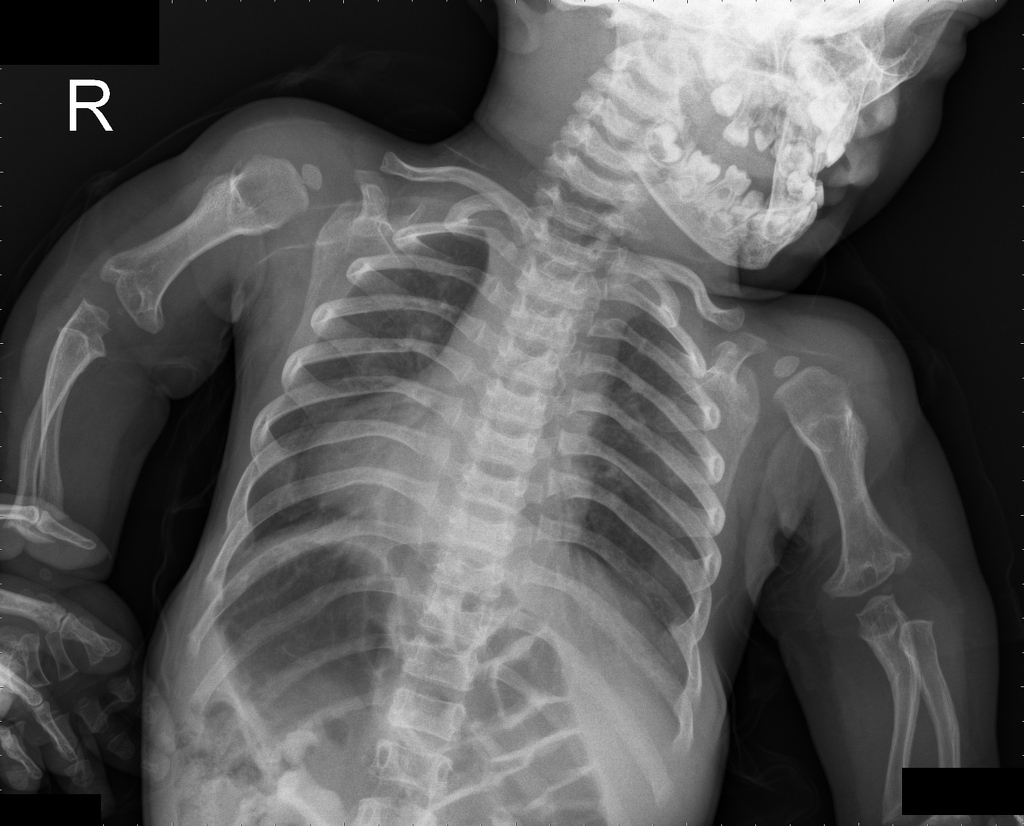
The diagnosis of achondroplasia can be based on the typical physical features, the hallmarks of achondroplasia, evident at birth.
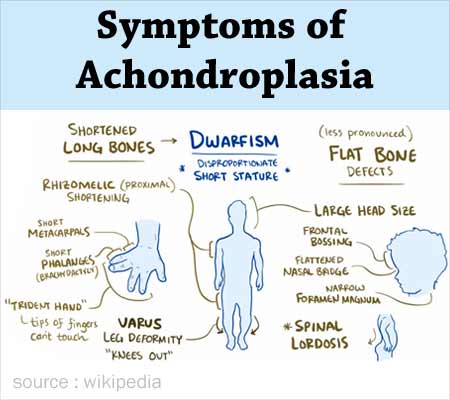
How to detect achondroplasia. If your doctor suspects achondroplasia, genetic. The following are the most common symptoms of achondroplasia; Shortened arms and legs, with the upper arms and thighs.
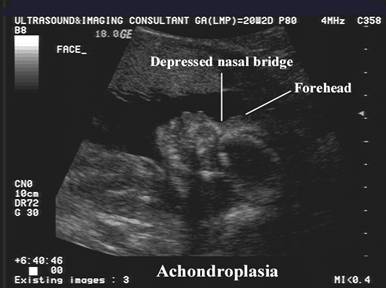
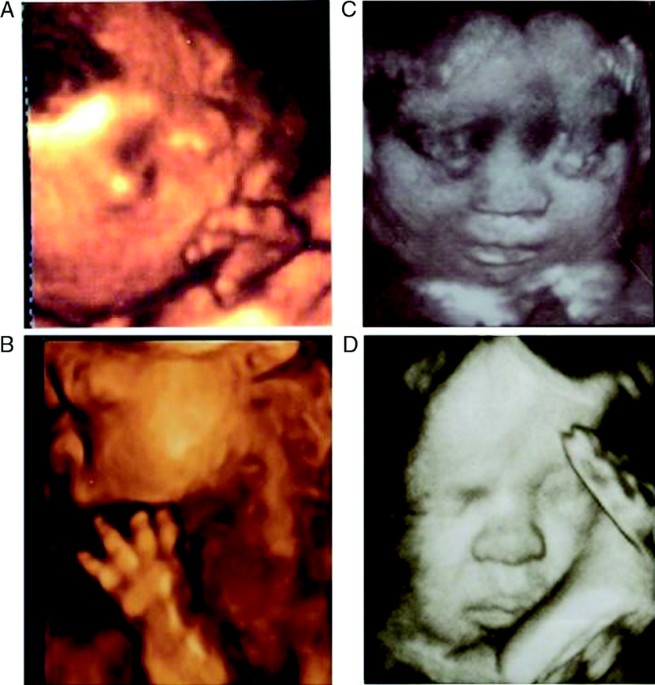
Your doctor might diagnose achondroplasia before birth using a fetal ultrasound or after birth through a physical examination and complete review of family medical history. We offer prenatal genetic screening and testing that may detect achondroplasia in the first trimester, which is much earlier than an ultrasound can detect it. This is done by obtaining a sample of dna from a person, typically through a blood draw.
Dna testing can also be. The diagnosis can be made by invasive testing or. However, each child may experience the condition differently:
Achondroplasia is due to a mutation in the fgfr3 gene and has autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. These include hydrocephalus, or an abnormally large head. Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of achondroplasia, but is not required for the diagnosis.
Some characteristics of achondroplasia are detectable during an ultrasound. In addition, the vet will need to do lab tests on the dog. The various signs and symptoms associated with achondroplasia differ according to age.
Prenatal examination (if one or both parents are affected). Dwarfism can result from a hundred different causes. Achondroplasia can be diagnosed before birth by fetal ultrasound.